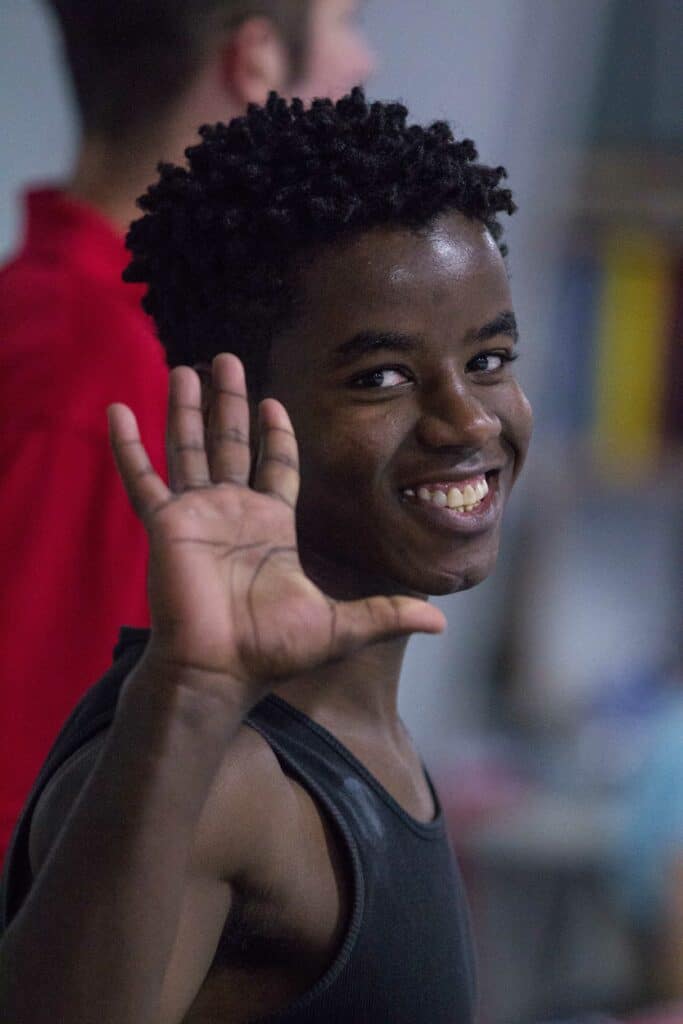
There is a well-established link between physical activity and overall health, and this connection is even more vital when we talk about children. Numerous studies highlight that regular physical exercise can have multiple benefits for children, contributing to their overall well-being, reducing the risk of various diseases, and fostering a healthier lifestyle. Keeping our kids fit truly is the best offense against sickness, and here’s why.
The Foundation of Health
Physical activity serves as a crucial building block for children’s health. It boosts their immune system, aids in the development of strong muscles and bones, reduces the risk of developing obesity, and even helps improve their mental health by reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Regular exercise doesn’t mean that your child needs to be an athlete or engage in high-intensity workouts. Simple activities like walking, cycling, playing outdoor games, or participating in sports activities at school can significantly enhance their physical health.
A Strong Immune System
An active body cultivates a strong immune system. Exercise promotes good circulation, which allows the cells and substances of the immune system to move through the body freely and do their job efficiently. Studies show that moderate, regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of catching colds and flu by boosting the body’s defense against bacteria and viruses.
Building Strong Bones and Muscles
During childhood and adolescence, bones are responsive to exercise, and physical activity can lead to an increase in bone density and strength. Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing activities like running or playing basketball, can benefit children’s bone health significantly. Not to mention, physical activity also helps children build healthy muscles, which support body movement and coordination.
Preventing Obesity
Childhood obesity is a serious public health problem that affects children and adolescents. Physical activity plays an important role in energy balance and weight control. Encouraging children to be active from a young age helps establish healthy habits, reduces the risk of becoming overweight or obese, and protects against related health problems later in life, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Mental Health Benefits
Physical activity isn’t just about the body; it’s equally essential for mental well-being. Regular exercise can help children manage stress, reduce feelings of anxiety and depression, improve their self-esteem, and enhance their overall mood. Exercise stimulates the production of endorphins, chemicals in the brain that act as natural mood lifters. Also, it provides children with better sleep, which is vital for their growth, development, and daily performance.
Promoting a Healthy Lifestyle
Physical activity habits established in childhood often carry into adulthood, making it a perfect time to instill the exercise habit. By teaching children the importance of being active, we’re equipping them with the tools to lead healthy, active lives as adults.
Keeping kids fit and healthy does require effort and encouragement from parents, caregivers, and educators. It’s about creating an environment that supports active lifestyles and providing opportunities for children to engage in physical activities they enjoy. It could be as simple as going for a family walk after dinner, encouraging participation in school sports teams, or trying out different activities like dance, swimming, or martial arts.
In conclusion, the benefits of physical activity for children’s health are vast and enduring. Keeping kids fit indeed is the best offense against sickness. Let’s take the initiative to promote a healthier future for our children by encouraging regular physical activity from an early age. The positive effects of a fit and active lifestyle on children’s health are too significant to ignore, making the correlation between physical activity and children’s health an essential part of their development.